how do leucine zippers work
Chargedpolar AAs via water mediated H bond ad 3. How do helices dimerize in a leucine zipper.
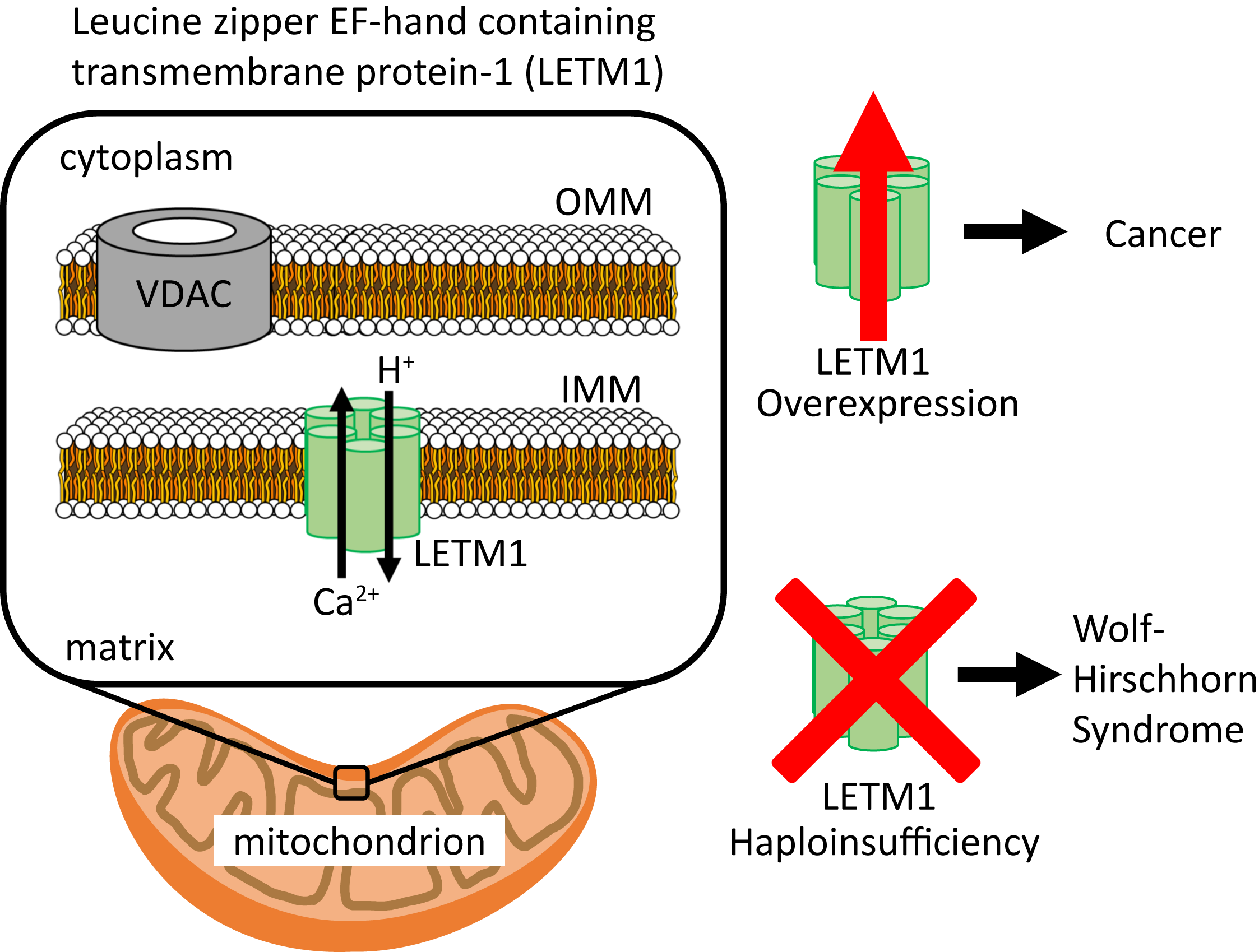
Ijms Free Full Text Molecular Mechanisms Of Leucine Zipper Ef Hand Containing Transmembrane Protein 1 Function In Health And Disease Html
In this article well examine the various parts that make up a zipper and see how these components lock together so easily and securely.

. The Leucine Zipper and the Basic DNA-Binding Domain bZIP This leucine zipper facilitates the dimerization of the protein by interdigitation of two leucine containing helices on different molecules and these residues form the buried subunit interface of the coiled-coil dimer. What does the leucine zipper do. The dimer interface of a leucine zipper involves side chains of the residues at the a d e and gpositions of the abcdefgnheptad repeat.
The zipper is so effective and reliable that in less than a hundred years it has become the de facto fastener for thousands of different products. Adding a leucine supplement to your diet can go a long way to mitigating the effects of a sub-optimal diet. Knobs into holes side chain packing.
Leucine zippers have a characteristic leucine repeat. Nature - Action of leucine zippers. D-leucine is the mirror image of L-leucine which is created in the laboratory and is also used as a supplement.
The polypeptide segments containing these periodic arrays of leucine residues are proposed to exist in an alpha-helical conformation and the leucine side chains extending from one alpha helix interdigitate with those displayed from a similar alpha helix of a second polypeptide facilitating dimerization. On dimerization the leucine-zipper a helices form a parallel-coiled coil based on hydrophobic interfacial side-chain packing 55. Non-polar AAs via hydrophobicity ad 2.
Leucine zipper is created by the dimerization of two specific alpha helix monomers bound to DNA. This hypothetical structure is referred. The leucine repeat in the sequence has been traditionally used for identification however with poor reliability.
The system is ingenious in its simplicity. DNA Binding and Phosphorylation Regulate the Core Structure of the NF-κB p50 Transcription Factor. The leucine zipper is a dimeric parallel coiled-coil but amphipathic helices can also oligomerize to form parallel coiled-coils that are trimers tetramers or pentamersThe majority of B-ZIP leucine zippers contain valines in the a positionandleucinesinthedpositionKimandcolleagues changed both of these amino acids to isoleucine which.
How does a leucine zipper work. There have been a large number of experimental studies that. The leucine zipper is the dimerization domain of the B-ZIP basic-region leucine zipper class of eukaryotic transcription factors Vinson et al 1989.
Up to 10 cash back The leucine zippers may be homo- or heterodimeric and thus increase their specificity by a combinatorial control mechanism. It does however optimize the results of your hard work. The leucine zipper structure is adopted by one family of the coiled coil proteins.
The binding domain is usually 100-amino-acid long. The leucine zipper is formed by amphipathic interaction between two ZIP domains. However many sequences have the leucine repeat but do not adopt the leucine zipper structure we shall refer to these as non-zippers.
These amino acids are spaced out in each regions polypeptide sequence in such a way that when the sequence is coiled in a 3D alpha-helix the leucine residues line up on the same side of the helix. These leucines together with the intervening residues form a zipper-like structure that dimerizes with the corresponding region of a partner bZIP protein. The leucine zipper is a dimerization domain occurring mostly in regulatory and thus in many oncogenic proteins.
These leucines are critical for the dimerization and DNA binding of B-ZIP proteins. Leucine zipper is created by the dimerization of two specific alpha helix monomers bound to DNA. The name arose because leucines occur every seven amino acids in this dimerization domain.
Leucine zippers contain a leucine in the d posi-tion of the repeating heptet 4 43 and can formwx homodimers eg as in GCN4 21 or het-wx erodimers eg as in Fos-Jun 21 51wx. Leucine Zippers Toshio Hakoshima Nara Institute of Science and Technology Nara Japan The leucine zipper ZIP motif consists of a periodic repetition of a leucine residue at every seventh position and forms an a-helical conformation which facilitates dimerization and in. The basic leucine zipper bZIP contains 25 conserved amino acids of these nine substitutions and disrupts function.
Up to 10 cash back The zipper region is an amphipathic helix of 3040 residues with every seventh residue a leucine. It may even be able to counteract the natural increase of fat tissue that occurs with aging. Regulation of gene expression by many transcription factors is controlled by specific combinations of homo- and heterodimers through a short α-helical coiled-coil known as a leucine zipper.
What do leucine zippers do during transcription regulation. L-leucine is the natural version of the amino acid is found in the proteins of the body and is the main form used as a supplement. The leucine zipper ZIP motif consists of a periodic repetition of a leucine residue at every seventh position heptad repeat and forms an α-helical conformation which facilitates dimerisation and in some cases higher oligomerisation of proteins by forming a parallel helixhelix association stabilised by formation of an interhelical hydrophobic core involving.
Leu-XLeu-X-Leu-X-Leu where X may be any residue. The ZIP domain is found in the alpha-helix of each monomer and contains leucines or. The leucine zipper is an amphipathic a helix containing heptad repeats of Leu residues on one face of the helix and serves as a dimerization module.
Ranging in length from about 14 to 45 residues they are far shorter than other coiled coils 43wx. The leucine zipper ZIP motif consists of a periodic repetition of a leucine residue at every seventh position and forms an α-helical conformation which facilitates dimerization and in. Abstract The leucine zipper ZIP motif consists of a periodic repetition of a leucine residue at every seventh position and forms an α-helical conformation which facilitates dimerization and in s.
Long charged AAs via electrostatic interaction eg 4. Despite the popularity of leucine among gym enthusiasts the science to back up most of its uses is weak. Leucine can prevent the buildup of fatty tissue on the body as well.
The coiled coil structure of a leucine zipper is required for dimerization and can be predicted with reasonable accuracy by existing algorithms.

Crystal Structure Of The Cgmp Dependent Protein Kinase Ii Leucine Zipper And Rab11b Protein Complex Reveals Molecular Details Of G Kinase Specific Interactions Journal Of Biological Chemistry
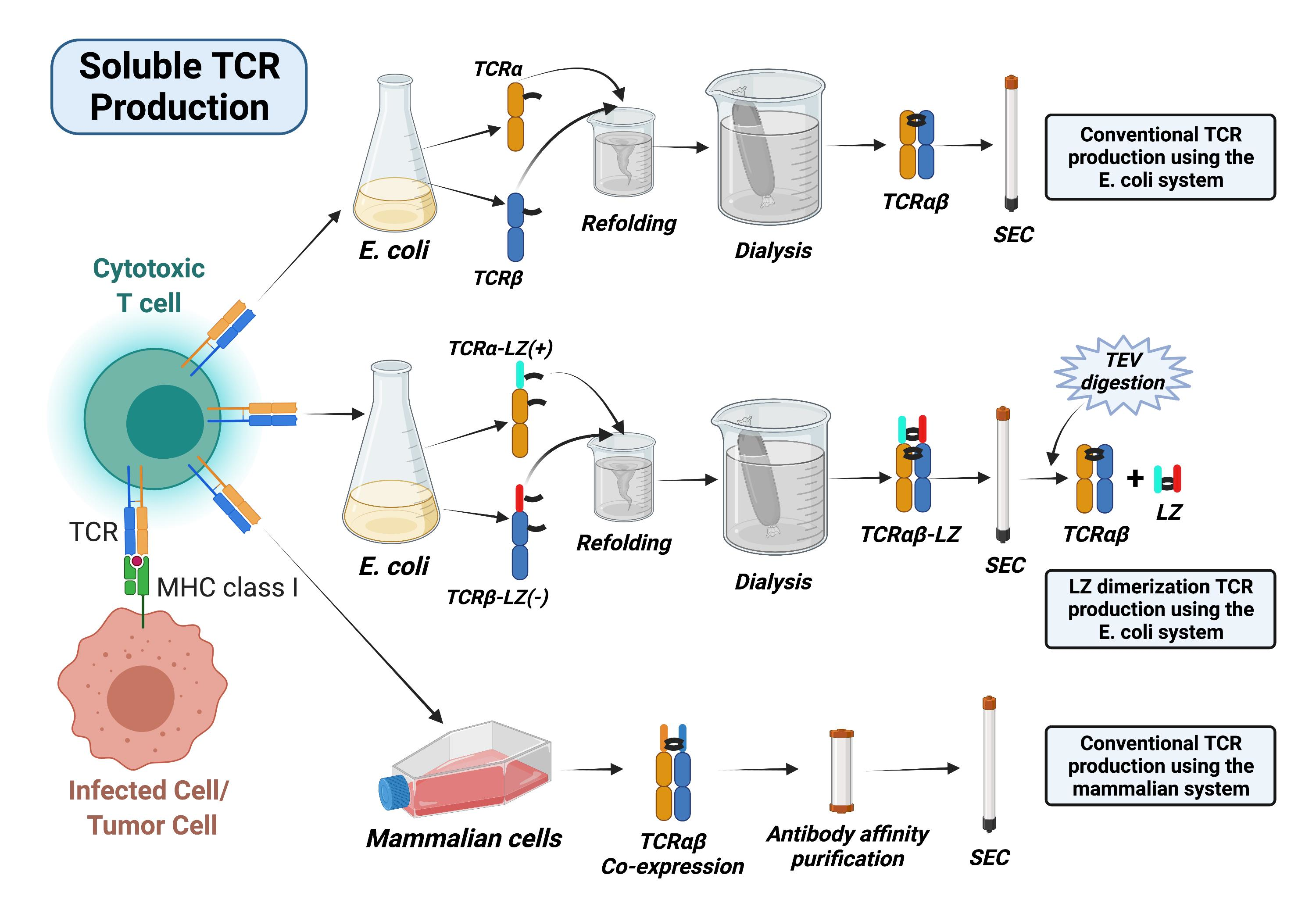
Cells Free Full Text A Leucine Zipper Dimerization Strategy To Generate Soluble T Cell Receptors Using The Escherichia Coli Expression System

A Interactions Between Anti Parallel Leucine Zippers Lz Dashed Download Scientific Diagram

Nrf2 Possesses A Redox Insensitive Nuclear Export Signal Overlapping With The Leucine Zipper Motif Journal Of Biological Chemistry

Amino Acid Sequence Of 7 Human Leucine Zipper Regions Proteins Are Download Scientific Diagram

Amino Acid And Nucleotide Sequence Of The Fos Leucine Zipper A And Of Download Scientific Diagram

Crystal Structure Of The Ccaat Box Enhancer Binding Protein B Activating Transcription Factor 4 Basic Leucine Zipper Heterodimer In The Absence Of Dna Journal Of Biological Chemistry

Helical Wheel Representation Of The Leucine Zipper Domain Of The Download Scientific Diagram

X Ray Structure Of Gcn4 B Zip Dimer Bound To Double Stranded Dna 10 Download Scientific Diagram
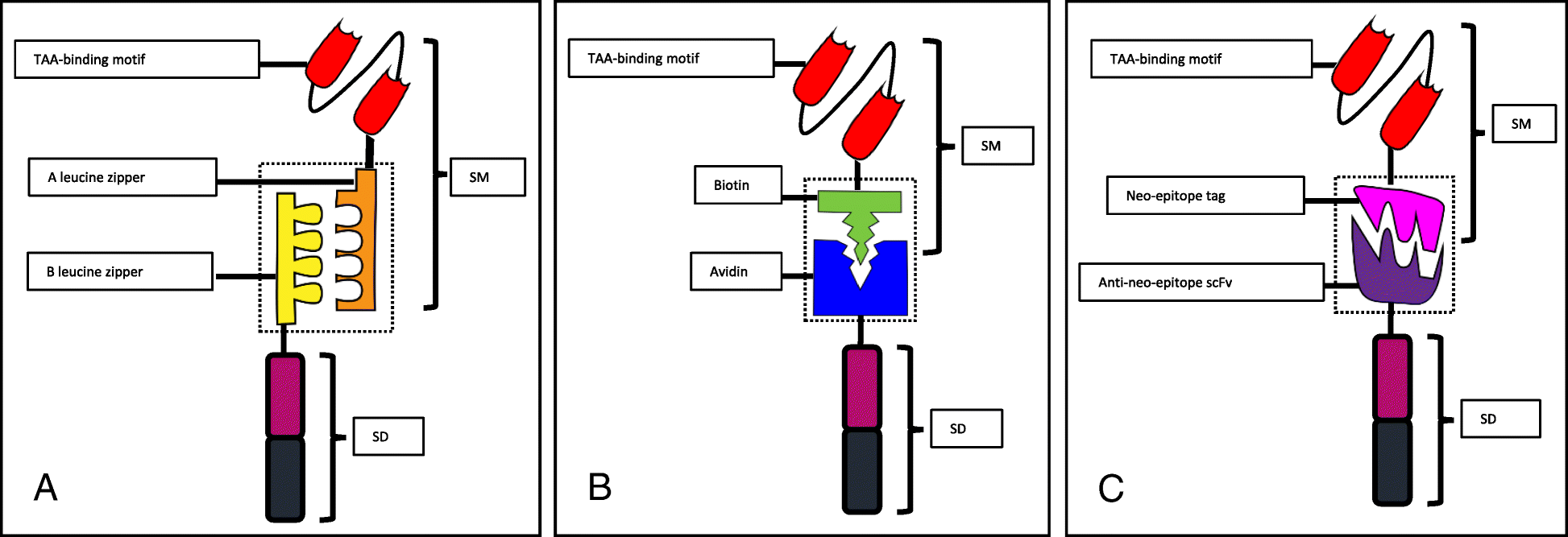
Engineering Switchable And Programmable Universal Cars For Car T Therapy Journal Of Hematology Oncology Full Text
Fosb Jund Bound To Cognate Dna A Bzip Domain With Leucine Zipper And Download Scientific Diagram

Basic Leucine Zipper Motif An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Leucine Zipper Domains Designed For High Affinity Heterodimerization Download Scientific Diagram

Attractive Interhelical Electrostatic Interactions In The Proline And Acidic Rich Region Par Leucine Zipper Subfamily Preclude Heterodimerization With Other Basic Leucine Zipper Subfamilies Journal Of Biological Chemistry

Leucine Zipper Mediated Homodimerization Of The P21 Activated Kinase Interacting Factor Bpix Journal Of Biological Chemistry

Amino Acid Sequence Of 7 Human Leucine Zipper Regions Proteins Are Download Scientific Diagram


